Take a look at the 5 posts on our blog in the field of ADME-Tox that saw the most visits in 2014!
#5 – Modulate hepatic inflammation
 Kupffer cells are macrophages endogenous to the liver which have the ability to modulate hepatic inflammation and injury associated with various pathophysiologies and toxicities. Pro-inflammatory cytokines released by activated Kupffer cells, such as TNF-α and IL-6, are associated with up-regulation of acute-phase response proteins and suppression of CYP enzymes.
Kupffer cells are macrophages endogenous to the liver which have the ability to modulate hepatic inflammation and injury associated with various pathophysiologies and toxicities. Pro-inflammatory cytokines released by activated Kupffer cells, such as TNF-α and IL-6, are associated with up-regulation of acute-phase response proteins and suppression of CYP enzymes.
#4 – Maximise availability & reduce variability in hepatocytes studies
 Pooled human hepatocytes are a preferred test system in many drug discovery and development applications which require intact cellular systems for in vitro testing. Intact hepatocytes contain the major hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes and co-factors required to evaluate the metabolism and potential drug-drug interactions of drug candidates effectively.
Pooled human hepatocytes are a preferred test system in many drug discovery and development applications which require intact cellular systems for in vitro testing. Intact hepatocytes contain the major hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes and co-factors required to evaluate the metabolism and potential drug-drug interactions of drug candidates effectively.
Over the last decade, improvements of cryopreservation technologies make possible using cryopreserved human hepatocyte more conveniently. Pooled cryopreserved hepatocytes reduce the inter-individual differences and polymorphic distribution of liver enzymes. However, this is crucial to carefully select a pool according to its performance but also the application used for.
#3 – in vitro exploration of hepatobiliary drug disposition
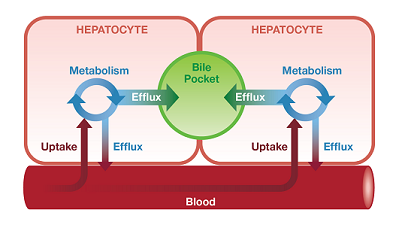
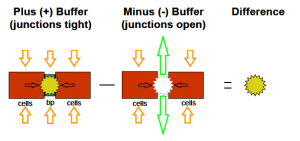 To obtain a true in vivo understanding of hepatic disposition and drug interactions, all three major clearance pathways (uptake, metabolism, and efflux) must be present, ideally, within the same model system. A system that integrates these three pathways together can assess cellular compensation effects, which mirrors the in vivo situation.
To obtain a true in vivo understanding of hepatic disposition and drug interactions, all three major clearance pathways (uptake, metabolism, and efflux) must be present, ideally, within the same model system. A system that integrates these three pathways together can assess cellular compensation effects, which mirrors the in vivo situation.
#2 – 6 tips for thawing hepatocytes
 Cryopreserved hepatocytes contain the major hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes required to study the four categories of xenobiotic biotransformation: hydrolysis, reduction, oxidation and conjugation. Cryopreserved hepatocytes are ready when you are. A simply quick-thaw protocol is performed to remove cryoprotectant and have viable cells… However, the functionality and the viability of these cells can be impaired by an incorrect thawing procedure…
Cryopreserved hepatocytes contain the major hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes required to study the four categories of xenobiotic biotransformation: hydrolysis, reduction, oxidation and conjugation. Cryopreserved hepatocytes are ready when you are. A simply quick-thaw protocol is performed to remove cryoprotectant and have viable cells… However, the functionality and the viability of these cells can be impaired by an incorrect thawing procedure…
#1 – Plateable Hepatocytes… the “one cell type doesn’t fit all” syndrome
 Hepatocytes are commonly used in drug discovery and preclinical drug development to perform experiments requiring intact cellular systems. Intact hepatocytes contain the major hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes required to study the four categories of xenobiotic biotransformation: Hydrolysis, Reduction, Oxidation and Conjugation. Because of these enzymes, hepatocytes provide a viable and cost-effective alternative to in vivo compound testings.
Hepatocytes are commonly used in drug discovery and preclinical drug development to perform experiments requiring intact cellular systems. Intact hepatocytes contain the major hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes required to study the four categories of xenobiotic biotransformation: Hydrolysis, Reduction, Oxidation and Conjugation. Because of these enzymes, hepatocytes provide a viable and cost-effective alternative to in vivo compound testings.
However one type of hepatocytes lot doesn’t fit all!
Which topics caught your interest the most in 2014? And what will you be looking out for in 2015? Share your thoughts and comments with other researchers below!