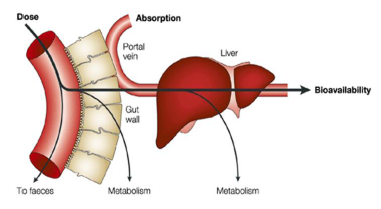
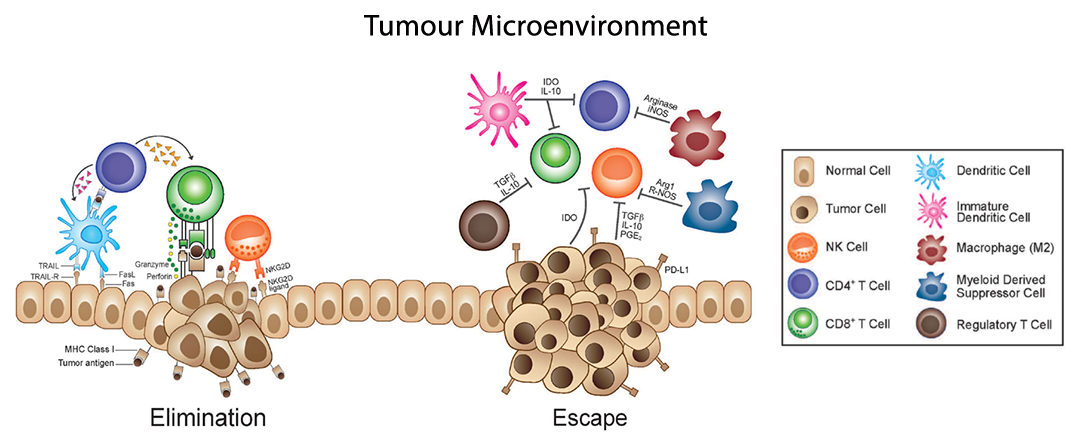
For years, we already knew that a lot of biomarkers are circulating in the blood (i.e. the secretome), as if it were a massive highway. Cells (apart from haematological cells, that is) also circulate.
There is much research now being focused on the role of several types of circulating cells in different diseases. Rapid advances in CRC research are pushing their utility to the in vitro diagnostic (IVD) arena, specifically in non-invasive diagnoses, companion diagnostics, and therapeutic monitoring. Up to date, several circulating rare cell (CRC) types have been described: Circulating Stem Cell (CSC), Circulating Endothelial Cell (CEC), Circulating Hematopoiectic Stem & Progenitor Cell (CHSPC), Circulating Mesenchymal Cell (CMC) and Circulating Tumour Cell (CTC).
Role of these CRCs still has to be elucidated, but there are some things we already know. For example, CSCs have a role in epithelial tumours & metastasis, as well as leukemia & lymphoma, together with CHPSCs and CTCs. CECs play a role in some tumour types. For cardiovascular, neurodegenerative and autoimmune diseases, CECs, together with CMSCs seem to be also involved.
Major challenges for the research on these CRCs is the optimisation of isolation methods, to make sure that we are indeed isolating CRCs and not other cell types. Current isolation methods depend on surface markers specific for these cell types, including EPCAM (1), CD44 (2), CD34 (3), CD38 (4), CTNNB1 (5), etc.
Working on CRCs and their role in your disease? Leave your comments below!
References
1.- Zhao, M. et al. Anal Chem. Oct 15, 2013; 85(20). doi: 10.1021/ac401985r.
2.- Qin, J. et al. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014; 7(6): 3235–3244. PMCID: PMC4097256.
3.- Sho, E. et al. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 2004; 24: 1916-1921.doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000142805.20398.74.
4.- Ferrero, E. & Malavasi, F. J Leukoc Biol. 1999 Feb;65(2):151-61.
5.- Nowak, M. et al. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2007;45(3):233-8.