Ras and Rho family members are small G proteins involved in the regulation of actin-dependent cell processes such as motility, growth, and intracellular trafficking. Furthermore, dysfunctions of Ras and Rho proteins are known to be correlated with a number of diseases (cancer, neurodegeneration).
Ras and Rho family members are small G proteins involved in the regulation of actin-dependent cell processes such as motility, growth, and intracellular trafficking. Furthermore, dysfunctions of Ras and Rho proteins are known to be correlated with a number of diseases (cancer, neurodegeneration).
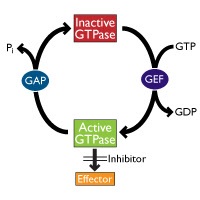
Small G proteins cycle between the inactive, GDP-bound form and the active, GTP-bound form.
G-LISA technology: state of the art small G protein activation measurement
Cytoskeleton, Inc. offers activation kits for a number of small G proteins (RhoA, Rac1, Cdc42, Ras, RalA, Arf1, Arf6). All these assays are available as G-LISA formats, a 96 well based technology, in which a protein sequence specifically binding to the activated for of the respective small G protein is coupled to the bottom of the wells and “catches” activated, GTP-bound proteins from cell lysates derived from cultured cells. The activation status of the small G protein can thus be detected in an ELISA like, quantitative approach.
A number of recently published papers using Cytoskeleton’s G-LISA kits show that not only RhoA and Rac1 can be measured with the RhoA-G-LISA and Rac1 G-LISA, respectively. By changing the antibody which is finally used to detect the activated small G protein bound to the binding protein one can e.g. differentiate between the isoforms RhoA, RhoB, and RhoC, and even RhoJ (which shows a high homology with Cdc42).
In their November newsletter Cytoskeleton Inc. summarized these publications and give valuable information and tips how to broaden the target specificity of their G-LISA kits.
Download your free copy of the newsletter GTPase Activation Assays: Detecting Different Isoforms
Any questions about using G-LISA? Fire away below!