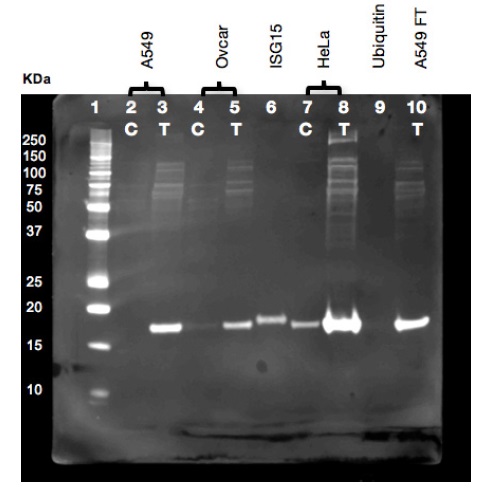
ISG15 ubiquitin-like modifier (ISG15) functions intracellularly as a Ubiquitin homologue and a cytokine. ISG15 induces production of IFN-gamma and augments NK/lymphokine-activated killer cell proliferation and function. Secreted from monocytes and lymphocytes, low levels of ISG15 are present constitutively in PBMCs. Interestingly, a dose-dependent ISG15 synthesis has been observed in response to IFN-alpha or IFN-beta, but not IFN-gamma.

For instance, ISG15 is secreted in response to IFN-beta treatment in vitro in healthy volunteers, as seen by measuring ISG15 serum levels (1). A process mediated by ISG15, ISGylation, has been described to have a role in immunomodulation after bacterial infection (2). HCV also induces ISG15 expression (3).
Briefly, ISG15 expression seems to regulate, at least in part, Type I interferon signaling, translation, chromatin remodeling, cell motility, protein trafficking, and protein conjugation (ISGylation). Still, the complete spectrum of ISG15-dependent biological sequelae re-mains to be fully elucidated.
Further characterization of new ISG15 target proteins and the role of free ISG15 may offer new insights into mechanistic and immuno-therapeutic approaches to human diseases.
Tools to detect ISG15 should be able to detect both bound and free-ISG15, and have no cross-reactivity with ubiquitin (e.g. anti-human ISG15, clone 2.1), as this may hinder the interpretation of results found with biological samples.
References
- D’Cunha, J. et al. Journal of Immunology, 1996, 157:4100.
- Dieterich, C. & Relman, D.A. PLoS ONE 6(11): e27535. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027535.
- Arnaud, N. et al. PLoS Pathog, 2011, 7(10): e1002289. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002289.
Studying the role of ISG15 in your experimental model?
Leave a comment regarding the research tools you are using to investigate the role of ISG15 in IFN signaling pathway !