Kupffer cells are macrophages endogenous to the liver which have the ability to modulate hepatic inflammation and injury associated with various pathophysiologies and toxicities. Pro-inflammatory cytokines released by activated Kupffer cells, such as TNF-α and IL-6, are associated with up-regulation of acute-phase response proteins and suppression of CYP enzymes.
For new biological entities, particularly immunomodulators, evaluating the potential for Kupffer cell activation is an emerging concept in preclinical development. Kupffer cells are estimated to comprise approximately 4-8% of total liver cell content and approximately 20% of non-parenchymal cells (Raccanelli and Rehermann, 2006).
tebu-bio and XenoTech offer Kupffer cells to aide in the assessment of cytokine release by biologics and small molecule drugs. Our Kupffer cells have been characterized for the following:
- Cell viability and cell yield (by Trypan blue staining)
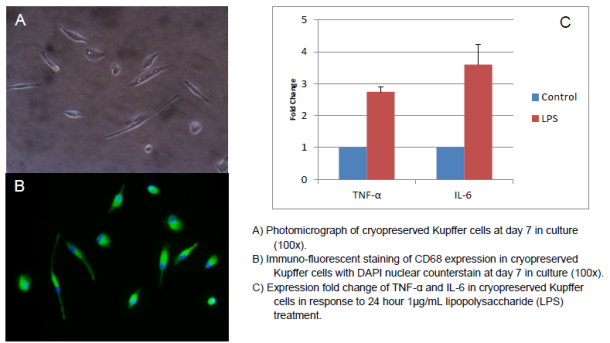
- Functionality: Activation by bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) measured by induction of Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-a) and Interleukin-6 (IL-6) mRNA and protein levels
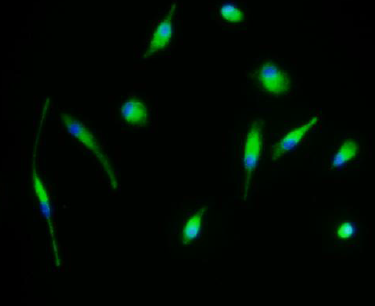
- Purity: Expression of macrophage marker CD68 (by Immuno-fluorescent microscopy)
Human cryopreserved Kupffer Cells
| Product | Description | Amount | AMY |
|---|---|---|---|
| HK1000.H15 | Cryopreserved Human Male Kupffer Cells | 1.0 mL | 1M cells |
| HK1500.H15 | Cryopreserved Human Female Kupffer Cells | 1.0 mL | 1M cells |
Freshly isolated cells
You can also get non-parenchymal liver population from freshly isolated liver sections. Get in touch with mycells@tebu-bio.com for detailed information.
For mouse or rat, there is also the Liver Dissociation System 3, which contains and engineered enzyme dissociation cocktail.