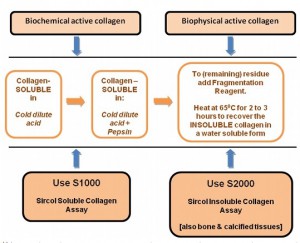
 Fig.1: Collagen source and Sircol assay choice.
Fig.1: Collagen source and Sircol assay choice.Matrix components are key R&D elements in pharmaceutical and cosmetology with tremendous impacts on tissue regeneration, skin repair, wound healing, allergy and inflammation, surgery, ageing diseases…
Collagen, Elastin, and Proteoglycans are major components of the Extracellular Matrix (ECM) where they form highly complex networks. ECM builds up an environment which supports surrounding cells and plays a crucial role in cell-to-cell communication, cell adhesion, and differentiation.
The monitoring of ECM components during experimental approaches requires robust and user-friendly in vitro assays. In the past experimental methods (e.g. soluble collagen measurement) were laborious and based on the use of harmful chemicals. Today, easy-to-use and straightforward methods with colorimetric read-outs are used daily.
ECM components #1: Soluble and insoluble Collagen
The Sircol Assay (Biocolor) is a quantitative dye-binding method designed for the analysis of Acid-Soluble Collagen (ASC) and Pepsin-Soluble Collagen (PSC) by absorbance readings within the range 520-570 nm. Furthermore, a variant of this kit uses mild acid and temperature treatment for 2 to 3 hours to denature insoluble collagen fibers and make them measurable with the Sircol dye. Types I to V mammalian collagens can be measured with the assays.
By applying both assays, the Sircol Collagen assay and the Sircol INSOLUBLE Collagen Assay, three collagen fractions can be differentiated (See Fig.1):
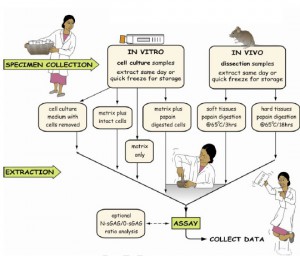 Fig. 2: Flowchart of the Blyscan assay.
Fig. 2: Flowchart of the Blyscan assay.- Collagen soluble in cold dilute acid
- Collagen soluble in cold dilute acid and pepsin
- Insoluble collagen
Of course, by adding the results together a value for the "Total Collagen" in a sample can be established.
ECM components #2: Glycosaminoglycans and Proteoglycans
The Blyscan assay (see flowchart Fig. 2) is a quantitative dye-binding method for the analysis of sulfated proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans.
Test material can be assayed directly when present in a soluble form, or following papain extraction from biological materials. The assay can be used to measure the total glycosaminoglycans content and can also be adopted to determine the O- and N-sulfated glycosaminoglycan ratio within test samples.
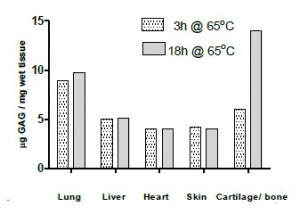 Fig. 3: Recovery of soluble glucosaminoglycans from mouse tissues, with 3 and 18 hours of hot papain.
Fig. 3: Recovery of soluble glucosaminoglycans from mouse tissues, with 3 and 18 hours of hot papain.The assay can be used from:
- fibrous and hyaline cartilages
- arteries, heart, lung, skin and other material containing extracellular matrix, (connective tissue) and solid tumours (results see Fig. 3)
- extracellular matrix components that may be released by live cells into the culture medium, some of which can be attached to cell culture plasticware
- soluble glycosaminoglycans from synovial fluid, urine and gel chromatography fraction aliquots
ECM components #3: Elastin
Similar to the Sircol and Blysan assays, the Fastin assay is a based on a colorimetric method utilizing the Fastin dye which binds to elastins released into tissue culture medium and extracted from biological materials. The kit measures:
- soluble tropoelastins
- athyrogenic elastins
- insoluble elastins (following solubilization to elastin polypeptides [α-elastin, κ-elastin])
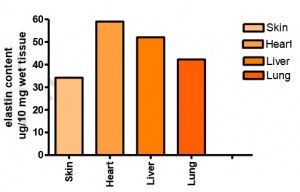 Fig. 4: The extracts shown were pooled and expressed as μg elastin per 10 mg wet tissue.
Fig. 4: The extracts shown were pooled and expressed as μg elastin per 10 mg wet tissue.
Typical results obtained with diverse mouse tissues are shown in Fig. 4.
Monitoring other ECM components?
Besides the colorimetric assay presented above, we can also offer ELISA based assays from ECM components such as hyaloronic acid, fibronectin and laminin.

